Home

With the resources of the SUNY Research Foundation, and our history of successful partnerships, we are here to help move biomedical products and ideas to market.

Our scientists and core facilities can help move discoveries into practice and technologies into the marketplace.

Upstate is home to top research facilities with highly specialized equipment and advanced instrumentation, to support research and product development.

We are here to create the relationships and partnerships needed to move innovative ideas forward.
Upstate Biotech Ventures
In a partnership between Empire State Development, Upstate Medical University, the SUNY Research Foundation, and Excell Partners, the newly-launched Upstate Biotech Ventures invests in high-potential startups and small businesses affiliated with Upstate Medical University to drive research and technology innovation.
Recent Tech from SUNY Upstate

A specially designed peptide blocks two key enzymes needed for ribosome production in cancer cells, ...
A specially designed peptide blocks two key enzymes needed for ribosome production in cancer cells, shutting down their protein-making machinery and offering a new, more effective way to treat cancer and prevent drug resistance. Background:
Ribosome biogenesis is a fundamental cellular process involving the coordinated synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and transfer RNA (tRNA), which are essential for protein production. In healthy cells, this process is tightly regulated to match physiological needs. However, in cancer cells, ribosome biogenesis is often dramatically upregulated to support the increased demand for protein synthesis required for rapid cell proliferation. This upregulation is driven by heightened activity of RNA Polymerase I (Pol I), which transcribes rRNA, and RNA Polymerase III (Pol III), which transcribes tRNA. Because of their central role in supporting malignant growth, both Pol I and Pol III have emerged as attractive targets for anti-cancer therapies, particularly in tumors characterized by high rates of protein synthesis. Despite the promise of targeting ribosome biogenesis, current therapeutic approaches are limited by their specificity; most available inhibitors are designed to act on either Pol I or Pol III, but not both. This single-target strategy presents a significant drawback: cancer cells can adapt by compensating with the uninhibited polymerase, thereby maintaining ribosome production and undermining the efficacy of the treatment. Additionally, the redundancy between Pol I and Pol III activity can contribute to the development of drug resistance, as tumor cells exploit alternative pathways to sustain their growth. These limitations highlight a critical need for more comprehensive strategies that can simultaneously disrupt both arms of ribosome biogenesis, thereby closing off compensatory mechanisms and improving therapeutic outcomes.Technology Overview:
A rationally designed peptide inhibitor has been developed to simultaneously target RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) and RNA Polymerase III (Pol III), two enzymes essential for ribosome biogenesis in cancer cells. This peptide works by disrupting the POLR1D/POLR1C heterodimer, a shared subunit interface crucial for the assembly and function of both polymerase complexes. By interfering with this common component, the peptide effectively suppresses the transcriptional activity of Pol I, which synthesizes ribosomal RNAs, and Pol III, which produces transfer RNAs—both necessary for protein synthesis and rapid cell proliferation. This technology is differentiated by its dual-targeting mechanism, which addresses a significant limitation of current therapies that inhibit either Pol I or Pol III alone. Single-polymerase inhibitors can be circumvented by cancer cells through compensatory upregulation of the uninhibited polymerase, reducing treatment efficacy and fostering drug resistance. By simultaneously shutting down both Pol I and Pol III, this peptide inhibitor provides a more comprehensive blockade of ribosome production, directly attacking a critical vulnerability in cancer cell metabolism. This approach not only promises enhanced therapeutic outcomes and reduced resistance but also opens new avenues for precision oncology, diagnostics, and the development of peptide-based therapeutics for other diseases involving aberrant transcriptional regulation. https://suny.technologypublisher.com/files/sites/adobestock_327332113.jpegAdvantages:
• Simultaneous inhibition of RNA Polymerase I and III enhances suppression of ribosome biogenesis in cancer cells.
• Reduces cancer proliferation by targeting a shared essential subunit interface (POLR1D/POLR1C) critical for polymerase assembly.
• Potentially lowers drug resistance by preventing compensatory upregulation of either polymerase.
• May reduce toxicity compared to single-target therapies through more precise dual inhibition.
• Applicable as a direct anti-cancer therapeutic and as a diagnostic tool for tumors with high Pol I/III activity.
• Provides a versatile peptide scaffold adaptable for other protein-protein interaction targets and drug delivery systems.
• Serves as a research tool for synthetic biology and gene expression modulation.
• Offers a platform for developing anti-microbial and anti-fungal agents targeting analogous polymerases in pathogens. Applications:
• Cancer therapeutics
• Precision oncology diagnostics
• Peptide drug development platforms
• Synthetic biology research tools Intellectual Property Summary:
Patent application 63/779,861 filed on 3/28/2025Stage of Development:
TRL 2Licensing Status:
This technology is available for licensing.
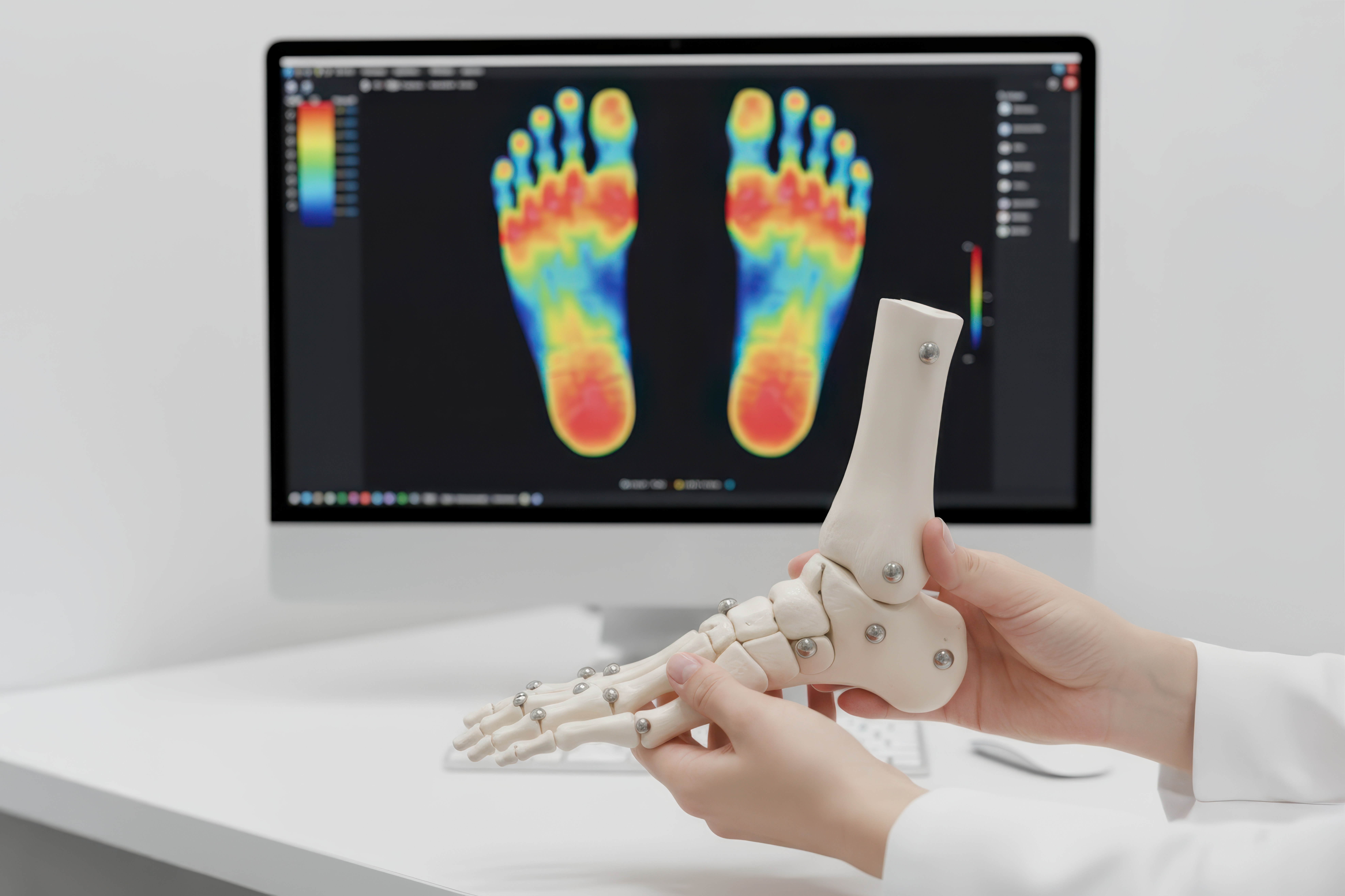
This technology enables diabetic patients to detect foot ulcers easily and effectively at home. Back...
This technology enables diabetic patients to detect foot ulcers easily and effectively at home. Background:
Diabetic foot ulcers are a significant health problem (15% baseline probability) in the growing diabetic population. Foot ulcers can become infected and lead to hospitalization or even amputation. The best way to address this disease is through prevention via inspection, in which a qualified medical professional examines a patient’s feet every three to six months, and determines whether a change in footwear or behavior is warranted. In between visits, patients are instructed to self-examine their feet. Unfortunately, these self-examinations can be ineffective for a variety of reasons. One issue contributing to patients not detecting a foot ulcer is diabetic neuropathy. Patients with advanced disease have little to no sensation in their distal limbs due to the loss of small nerves. Therefore, what should be an excruciating wound goes unnoticed.Technology Overview:
This technology is a device for monitoring the surface of the foot to detect early signs of tissue disruption. It captures images of the patient’s plantar surface in a streamlined and standardized manner. The previous record of images can be analyzed to detect changes in the integrity of the plantar surface tissue. Quantification of ulcer size is simplified by imaging the foot at a constant focal plane. The device can be used independently by patients at home without assistance. Data can be initially processed within the device as well as uploaded to the cloud for further analysis by a medical professional. https://suny.technologypublisher.com/files/sites/adobestock_1801631869.jpegAdvantages:
• Detects diabetic foot ulcers more accurately and effectively than patient self-examination.
• Addresses a major health risk among diabetics.
• Can provide data that can be uploaded to the cloud for analysis by health professionals.
• Easy to use at home by untrained patients. Applications:
The primary application for this technology is early detection of foot ulcers in diabetic patients. Patent application filed: US 20240341674, “Diabetic Foot Examination Device,” Filed April 15, 2024 (Application Number 18/635,398), published October 17, 2024Stage of Development:
TRL 3 – Experimental proof of conceptLicensing Status:
This technology is available for licensing.

This technology enables safer administration of radioligand therapies, allowing for healthier, lower...
This technology enables safer administration of radioligand therapies, allowing for healthier, lower radiation doses to both patients and administering staff. Background:
At present, there are two FDA-approved radioligand therapies for broad use in cancer treatment: Lutathera (177Lutetium DOTATATE) and Pluvicto (177Lutetium Vipivotide Tetraxetan). Pluvicto is dispensed from the pharmaceutical distributor in a 20cc syringe for intravenous injection. Currently, there is no way to allow physicians to hold this syringe within a syringe shield while administering the dose. And even with lead-lined gloves, the radiation the physician absorbs during the two-minute injection can be significant. Further, the syringe shield is not secure when grasped with lead-lined gloves. As a result, there is a tradeoff between secure administration and radiation exposure dose.Technology Overview:
This technology is a physical support device for safely administering radioligand therapies. This device, called a dose caddy, allows the syringe and syringe shield to fit snugly onto a larger physical mount that can fit onto a standard clinical tabletop. The syringe plunger extension rod and set up of the dose caddy minimize the radiation dose to the administering physician, while allowing safe, controlled delivery of the radiopharmaceutical to the patient. The dose caddy is printed via tabletop 3D printer, with ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) or PLA (Polylactic Acid) as the printing material. This device is highly configurable to any clinical setting and allows for safer, lower radiation doses to both patients and administering staff. https://suny.technologypublisher.com/files/sites/adobestock_255606405.jpegAdvantages:
• Protects physician from radiation during administration of radioligand therapies.
• Provides better control of syringe compared to using lead-lined gloves with a syringe shield.
• Highly configurable to the clinical setting.
• Can be fabricated via 3D printer, using common materials. Applications:
The primary application for this technology is safer administration of radioligand therapies. US Non-Provisional Filed: 19/394,230Stage of Development:
TRL 6Licensing Status:
This technology is available for licensing.

We anticipate that this topical treatment will increase genital sensitivity in women, facilitating s...
We anticipate that this topical treatment will increase genital sensitivity in women, facilitating sexual arousal and helping treat sexual dysfunction. Background:
As the population ages, there has been increased focus around sexual dysfunction as a medical issue. This has resulted in a number of successful treatments that ameliorate sexual dysfunction in men. However, treatments aimed at woman have not been nearly as effective. One of the reasons for this is that female sexual dysfunction is complex. At least one likely factor contributing to female dysfunction is diminished genital sensitivity arising from loss of sensory nerve fibers in the clitoris and vagina.Technology Overview:
This technology is based on the hypothesis that topical 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) may enhance the sensitivity of the sensory nerves in the genital region and increase female sexual arousal. This medication has already been approved for oral use to improve neuronal function in conditions where either peripheral nerves or central neurons have impaired transmitter release or defective axonal conduction. We believe that 4-AP’s ability to prolong action potentials and facilitate the repetitive firing of neurons will allow it to be used topically as a treatment for sexual dysfunction. https://suny.technologypublisher.com/files/sites/adobestock_5878419381.jpegAdvantages:
• Easy and safe topical application
• Uses medication that has already been approved for a different purpose. Applications:
The primary use for this technology is for treatment of female sexual dysfunction. Intellectual Property Summary:
Patent Issued: US10888552B2, “Treatment of disorders of sexual arousal with local application of agents that increase membrane excitability” (see also https://patents.google.com/patent/US10888552B2/en). Stage of Development:
TRL 2, Technology concept and/or application formulated.Licensing Status:
This technology is available for licensing.Licensing Potential:
This technology would be of interest to anyone involved in the treatment of female sexual dysfunction, including:
• Pharmaceutical companies.
• Hospitals.
• Health care providers.
• Medical research laboratories.




